What is a Burette?
A burette (often misspelled as burrette) is a precision instrument used in chemistry labs to deliver accurate and controlled volumes of liquid, especially during titration. Its high measurement accuracy allows scientists to add solution drop by drop, helping detect exact reaction endpoints and ensuring reliable analytical results.
Scientific Definition of Burette
A burette is a precision volumetric glassware instrument designed to dispense known volumes of liquid with high accuracy and control. It is primarily used in titration experiments, where one solution is gradually added to another until a chemical reaction reaches its endpoint.
Key scientific characteristics:
- Long, narrow, graduated glass tube
- Calibrated in milliliters (mL)
- Equipped with a stopcock valve for controlled flow
- Measures liquid delivered, not contained
In analytical chemistry, burettes are classified as Class A laboratory glassware, meaning they are manufactured to strict accuracy standards.
Burette Diagram Explained
Understanding the burette diagram is essential for using the instrument correctly.
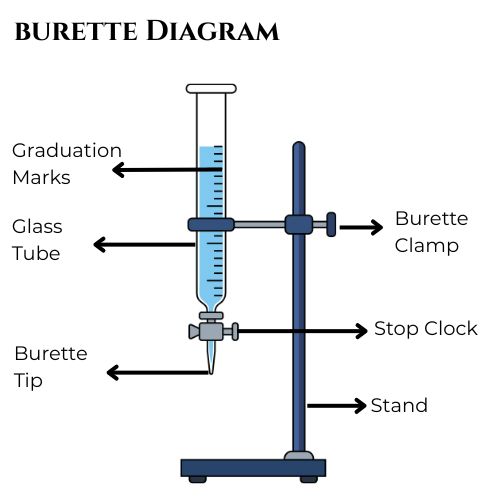
Labeled Burette Diagram
A burette consists of four main parts:
Glass Tube
The long vertical glass tube marked with graduation lines showing volume measurements.
Stopcock
A valve located at the bottom that controls liquid flow.
Burette Tip
A narrow outlet through which liquid is dispensed drop by drop.
Zero Mark
Located at the top of the graduated scale, indicating the starting volume.
History and Evolution of the Burette
The burette has a fascinating history dating back to the 18th and 19th centuries, when scientists began standardizing chemical analysis techniques.
Early milestones:
- 1791: French chemist François Antoine Henri Descroizilles created an early burette-like instrument for titration.
- 1845: Karl Friedrich Mohr improved the design by adding the stopcock, creating the modern burette.
- 20th century: Development of PTFE stopcocks and digital burettes improved durability and precision.
- Modern era: Automatic and digital burettes now enable ultra-precise industrial and pharmaceutical testing.
Today, the burette remains a symbol of precision analytical chemistry.
Working Principle Based on Burette Diagram

The burette works on a simple but precise principle:
- The burette is filled with a standard solution.
- The initial reading is recorded at the zero mark.
- The stopcock is opened to allow controlled liquid flow.
- The final reading is taken after titration.
- Volume delivered = Final reading − Initial reading.
This design ensures extremely accurate volume measurement, often up to ±0.05 mL.
Parts of a Burette and Their Functions
Understanding each part helps ensure proper usage and accuracy.
Graduated Glass Tube
This is the most visible component of the burette.
Functions:
- Holds the solution being dispensed
- Provides precise volume measurement
- Calibrated for high accuracy
The tube is narrow to improve reading precision and reduce measurement errors.
Stopcock (Glass / PTFE)
The stopcock is the control valve of the burette.
Types:
- Glass stopcock (traditional)
- PTFE stopcock (modern, chemical-resistant)
Functions:
- Controls liquid flow
- Allows dropwise dispensing
- Prevents leakage
Without the stopcock, precise titration would not be possible.
Burette Tip
The tip is the narrow outlet at the bottom.
Functions:
- Ensures smooth, drop-by-drop delivery
- Prevents splashing
- Improves endpoint detection accuracy
The tip is designed for controlled precision.
Burette Uses in Laboratory Applications
The burette uses extend across many scientific fields.
Use of Burette in Titration
Titration is the primary application.
Types of titrations:
- Acid–base titration
- Redox titration
- Complexometric titration
In titration, burettes allow scientists to determine unknown concentrations accurately.
Burette Uses in Chemistry Laboratories
In educational and research labs, burettes are used for:
- Preparing standard solutions
- Analytical chemistry experiments
- Quality control testing
- Chemical reaction studies
Every chemistry student learns burette usage early in laboratory training.
Use of Burette in Pharmaceutical & Research Labs
Pharmaceutical labs rely heavily on burettes for:
- Drug formulation analysis
- Quality testing of chemicals
- Research experiments
- Standardization of solutions
Accuracy is critical in pharmaceutical analysis, making burettes indispensable.
Types of Burette
Glass Burette
Traditional and widely used.
Advantages:
- High accuracy
- Chemically resistant
- Affordable
Ideal for schools and standard laboratories.
Digital / Automatic Burette
Modern and highly precise.
Features:
- Digital volume display
- Automatic dispensing
- Reduced human error
Used in industrial and pharmaceutical labs.
Micro Burette
Designed for small volume analysis.
Uses:
- Research labs
- Micro-chemical experiments
- High-value reagent testing
Perfect when only tiny volumes are required.
Burette Stand – Purpose and Importance
What is a burette stand?
A burette stand is a support structure that holds the burette vertically during experiments.
Functions:
- Keeps burette stable
- Prevents accidents
- Ensures accurate readings
Types of Burette Stand
Cast Iron Base
- Heavy and stable
- Ideal for professional labs
Wooden Base
- Lightweight and economical
- Used in schools
Adjustable Metal Stand
- Height adjustable
- Used in advanced labs
Why a Burette Stand is Essential in Titration
A burette must remain perfectly vertical for accurate readings. A stand ensures:
- Stability
- Safety
- Measurement accuracy
Without a stand, titration results may become unreliable.
How to Use a Burette Correctly
Step-by-Step Procedure to Use a Burette
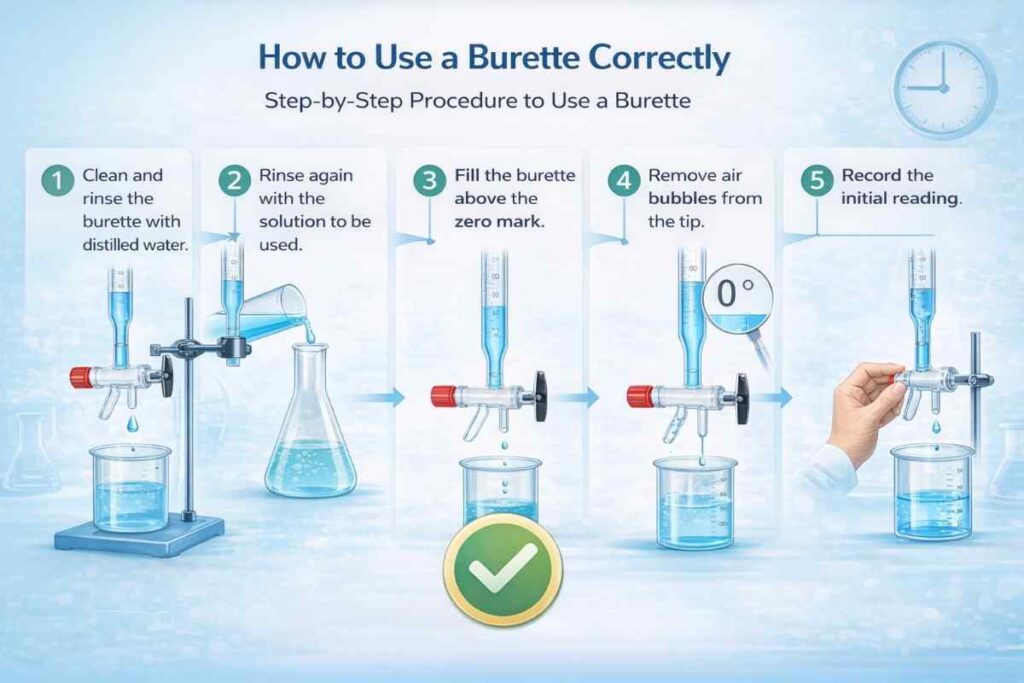
- Clean and rinse the burette with distilled water.
- Rinse again with the solution to be used.
- Fill the burette above the zero mark.
- Remove air bubbles from the tip.
- Record the initial reading.
- Open stopcock slowly to start titration.
- Record final reading at endpoint.
Common Mistakes While Using a Burette
Avoid these errors:
- Air bubbles in the tip
- Parallax error while reading scale
- Incorrect zero setting
- Fast liquid release
These mistakes reduce measurement accuracy.
Burette Price Guide
Burette Price Based on Type
Approximate ranges:
- Glass burette: Affordable
- Digital burette: Expensive
- Automatic burette: Premium range
Factors Affecting Burrette Price
Several factors influence Burrette Price:
- Material (glass vs plastic)
- Accuracy class (Class A or B)
- Brand reputation
- Calibration certification
Higher precision means higher cost.
Average Burette Price in India
Typical price range:
- Glass burette: ₹400 – ₹1500
- Digital burette: ₹15,000 – ₹50,000
- Automatic burette: ₹30,000 – ₹1,00,000
Prices vary depending on quality and brand.
Care, Cleaning and Maintenance of Burette
Proper Cleaning Method
Steps:
- Rinse with distilled water after use
- Avoid detergent residue
- Dry naturally in vertical position
Proper cleaning prevents contamination.
Storage and Handling Tips
To extend life:
- Store vertically
- Avoid physical shocks
- Protect from chemical residue
Proper care ensures long-term accuracy.
Wrapping Notes – Importance of the Burette in Analytical Chemistry
The burette remains one of the most trusted instruments in laboratories worldwide. From student experiments to pharmaceutical research and industrial quality testing, its role in accurate chemical measurement is unmatched. Understanding what is burette, its diagram, parts, uses, types, and price helps appreciate its importance in scientific analysis. Precision, reliability, and controlled liquid delivery make the burette an essential tool in modern analytical chemistry.
Whether you are a student, researcher, or laboratory professional, mastering burette usage ensures accurate, reliable, and reproducible results in every experiment.



Add comment