A conical flask is one of the most essential and widely used pieces of laboratory glassware. Whether you are in a school lab, chemical industry, research facility, or pharmaceutical setup, you will always find this flask on every workbench. Its distinct conical shape, narrow neck, and flat base make it ideal for mixing, heating, culturing, and storing chemicals or solutions safely.
This guide explains everything: what a conical flask is, its structure, conical flask diagram, applications, sizes, materials, and the conical flask price range in India.
What Is a Conical Flask?
A conical flask (also known as an Erlenmeyer Flask) is a type of laboratory flask designed with three signature features:

- A flat bottom
- A conical, tapered body
- A narrow cylindrical neck
This shape allows:
- Safe swirling and mixing without spilling
- Holding liquids securely
- Easy heating on burners or hot plates
- Simple measurement markings
It was invented in 1860 by Emil Erlenmeyer, which is why you may hear the term Erlenmeyer flask.
Conical Flask Diagram (Structure Explained)
Below is a descriptive conical flask diagram explanation (text-based for reference):
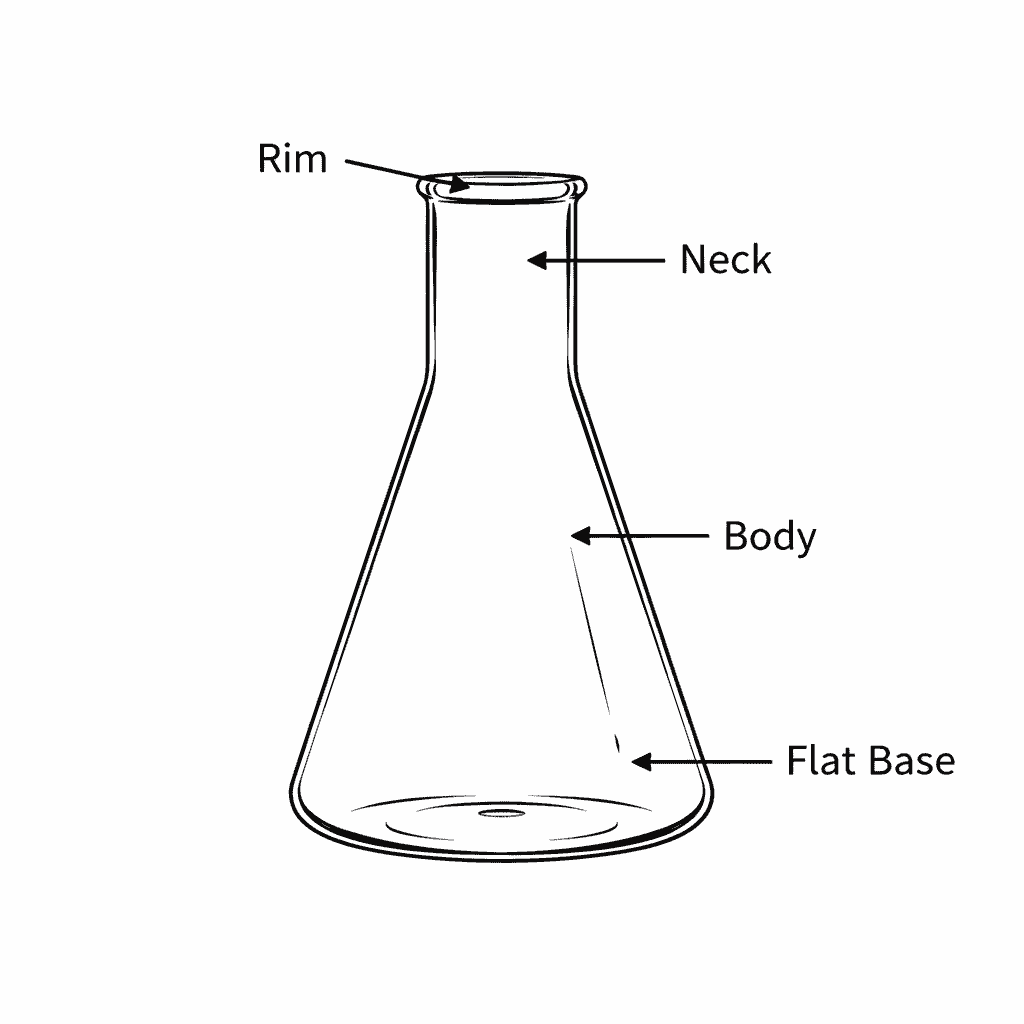
Main Parts of the Conical Flask
- Neck:
- Narrow and cylindrical
- Allows the user to grip and swirl solutions easily
- Prevents splashing during mixing
- Shoulder:
- The slanted part where the neck widens
- Helps control the flow when pouring liquids
- Conical Body:
- The wide, cone-shaped region
- Provides stability and room for mixing
- Flat Base:
- Allows the flask to stand upright
- Suitable for heating on hot plates
- Graduation Marks:
- Show approximate volume measurements
This structure is what makes the conical flask so versatile and safer than beakers for mixing or transporting chemicals.
Types of Conical Flasks
1. Based on Material
a) Borosilicate Glass Conical Flask
- Heat-resistant
- Chemical-resistant
- Ideal for schools, colleges, research labs
b) Plastic Conical Flask
- Made from PP or PC
- Unbreakable
- Used in fieldwork, microbiology, and industrial testing
2. Based on Design
a) Narrow Neck
- Most common type
- Suitable for titration, mixing, culturing
b) Wide Neck
- Allows easy addition of solids
- Preferred in industrial and chemical labs
c) Conical Flask with Stopper
- Comes with a glass or plastic stopper
- Suitable for storing prepared solutions
d) Conical Flask with Screw Cap
- Used for microbiology, PCR, and sterile applications
Common Sizes of Conical Flasks
Typical sizes include:
- 25 ml
- 50 ml
- 100 ml
- 150 ml
- 250 ml
- 500 ml
- 1000 ml (1 litre)
- 2000 ml (2 litre)
- 5000 ml (5 litre)
Laboratories choose sizes depending on the volume of solution needed for experiments.
Conical Flask Uses (Most Important Applications)
The list of conical flask uses is extensive because the design supports both simple and advanced laboratory processes.
1. For Mixing Solutions
Because of its narrow neck and wide base, the conical flask is perfect for swirling chemicals without spilling them. It is heavily used for:
- Preparing chemical solutions
- Diluting acids and bases
- Mixing reagents
2. For Heating Chemicals
Borosilicate flasks resist high temperatures. You can place the conical flask on:
- Bunsen burners
- Hot plates
- Heating mantles
It is used for boiling, sterilizing, and evaporating liquids safely.
3. In Titrations
In titration experiments:
- The conical flask holds the analyte
- The solution from a burette drips into it
- Its shape minimizes splashing during swirling
This is one of the most common conical flask uses in schools and colleges.
4. In Microbiology
Microbiologists use the flask for:
- Growing cultures
- Shaking incubation
- Preparing media
Flasks with screw caps or cotton plugs are preferred for sterile environments.
5. For Storage of Chemicals
Conical flasks with stoppers or caps help in temporary storage of:
- Buffers
- Culture media
- Prepared reagents
- Sample solutions
6. In Filtration
The conical flask is used with:
- Funnels
- Filter papers
- Buchner funnels (for vacuum filtration)
The narrow neck ensures secure funnel placement.
7. For Crystallization and Evaporation
Its shape allows slow evaporation, making it suitable for:
- Crystallizing chemicals
- Concentrating solutions
8. In Industrial and Quality Testing
Used for:
- Testing water and wastewater
- Checking chemical purity
- Industrial research and analysis
Advantages of a Conical Flask
- Minimizes spillage
- Easy to swirl solutions
- Safe for heating
- Stands stable on benches
- Good for growing cultures
- Compatible with funnels
- Available in many sizes
- Suitable for both liquid and solid chemicals
Difference Between Conical Flask and Beaker
| Feature | Conical Flask | Beaker |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Conical with narrow neck | Cylindrical with wide mouth |
| Mixing | Best for swirling without spilling | Easy to spill |
| Heating | More uniform heating | Slower heating |
| Filtration | Secure funnel placement | Funnel may slip |
| Applications | Titration, culturing, heating | General mixing & measuring |
Conical Flask Price in India (Complete Breakdown)
The conical flask price depends on:
- Size (ml)
- Material (glass or plastic)
- Brand
- Sterility
- Stopper or screw cap availability
Below is an estimated price guide (India):
Glass Conical Flask Price
| Size | Approx. Price (INR) |
|---|---|
| 50 ml | ₹40 – ₹80 |
| 100 ml | ₹50 – ₹120 |
| 250 ml | ₹70 – ₹150 |
| 500 ml | ₹90 – ₹250 |
| 1000 ml | ₹150 – ₹350 |
| 2000 ml | ₹300 – ₹750 |
| 5000 ml | ₹600 – ₹1500 |
Plastic Conical Flask Price
| Size | Approx. Price (INR) |
|---|---|
| 50–100 ml | ₹40 – ₹100 |
| 250 ml | ₹80 – ₹150 |
| 500 ml | ₹120 – ₹200 |
| 1000 ml | ₹150 – ₹300 |
Special Conical Flasks
| Type | Approx. Price |
|---|---|
| With Screw Cap | ₹200 – ₹900 |
| With Stopper | ₹120 – ₹450 |
| Sterile Conical Flask | ₹300 – ₹1200 |
Prices vary by brand such as Borosil, Glass Agencies, Labix, Micro Lab Equipment, and others.
How to Choose the Right Conical Flask
1. Choose Material Carefully
- Glass: For heating and chemical reactions
- Plastic: For unbreakable and microbial work
2. Select the Right Size
Pick a flask with at least 30% extra capacity for safe mixing.
3. Check for Graduation Accuracy
Choose ISO-certified brands for precise measurement markings.
4. Decide if You Need a Stopper
For storage or microbiological use, choose:
- Screw caps
- Glass stoppers
- Cotton plugs
5. Consider Heat and Chemical Resistance
Look for:
- Borosilicate 3.3 glass
- Autoclavable PP plastic
Maintenance & Safety Tips
- Do not heat plastic flasks unless they are autoclavable
- Avoid direct flame for thin-glass flasks
- Use gloves while handling hot flasks
- Clean immediately after use
- Check for cracks before heating
- Use brushes to clean narrow necks
- Store in safe racks to prevent breakage
Wrapping Notes
A conical flask is one of the most adaptable instruments in any laboratory. Its design is simple yet very effective. It is essential in mixing, heating, culturing, filtering, and storing solutions safely for school experiments and complex chemical studies alike.
Knowing the conical flask diagram, the construction, and the different conical flask involve the cost of conical flasks, all inform students, lab technicians, and researchers in the decision of which model is right for their purpose.
Frequently Asked Questions
A conical flask is mainly used for mixing, heating, storing, and culturing liquids in laboratories. Its narrow neck and conical shape allow safe swirling without spilling, which makes it ideal for titration experiments, preparing chemical solutions, growing microbial cultures, filtration, and heating on burners or hot plates.
A conical flask is also called an Erlenmeyer flask because it was invented in 1860 by German chemist Emil Erlenmeyer. The name honors his contribution to laboratory glassware design.
The price of a conical flask in India depends on size, material, and brand. Approximate price range:
50–100 ml: ₹40 – ₹120
250 ml: ₹70 – ₹150
500 ml: ₹90 – ₹250
1000 ml: ₹150 – ₹350
2000 ml: ₹300 – ₹750
5000 ml: ₹600 – ₹1500
Screw-cap or sterile flasks: ₹200 – ₹1200
Prices vary by brand such as Borosil, Labix, and other laboratory suppliers.
A conical flask has five main parts: the narrow neck (for gripping and swirling), the shoulder (for controlled pouring), the conical body (for mixing), the flat base (for stability and heating), and graduation marks (for approximate volume measurement).




Add comment